Bullish crypto traders maintain the upper hand despite the total market cap rejecting at $1T


Former BitMEX CEO Arthur Hayes says catastrophe is coming for the crypto sector, but derivatives data shows bulls slowly taking control of the market.
The total crypto market capitalization soared by 29.4% in two weeks, although Bitcoin’s (BTC) price stabilized near $21,000 on Jan. 19.
As a result, it became increasingly difficult to justify that the five-month-long bearish trend still prevails after the $930 billion total crypto channel top has been breached. Still, the psychological $1 trillion resistance remains strong.


The move possibly reflects investors becoming more optimistic about risk assets after weaker-than-expected inflation metrics signaled that U.S. Federal Reserve’s interest rate hiking strategy should ease throughout 2023.
However, Klaas Knot, who serves as the governor of the Dutch central bank, stated on Jan. 19 that the European Central Bank (ECB) “will not stop after a single 50 basis point hike, that’s for sure.”
At the Davos forum, Knot added: “Core inflation has not yet turned the corner in the Euro area.”
In essence, investors fear that another round of interest rate increases could further pressure corporate earnings, triggering unemployment and a deep recession. In this case, a sell-off on the stock market becomes the base scenario and the crypto markets would likely follow the bear trend.
To further prove the strong correlation between cryptocurrencies and the stock markets, the Russell 2000 index declined 3.4% between Jan. 18 and Jan. 19. The movement coincides with the total crypto market capitalization correcting by 4% after flirting with the $1 trillion mark on Jan. 18.
The 10.4% gain in total market capitalization between Jan. 12 and Jan. 19 was impacted mainly by Bitcoin’s 10.4% gains and Ether (ETH), which traded up by 8.7%. The bullish sentiment was more eventful for altcoins, with eight of the top 80 coins gaining 20% or more in the period.


Metaverse-related tokens rallied after tech giant Apple announced the upcoming release of its VR headset. Top movers included Decentraland (MANA), up 55%; Enjin (ENJ) rising 37%; and The Sandbox (SAND) climbing 30%.
Frax Share (FXS) rallied 40% as it reached 65,000 Ether deposited on its liquid staking protocol, which currently has over U$100 million in total value locked.
Privacy coins like Monero (XMR) and ZCash (ZEC) both declined after increased regulatory risks and the U.S. Department of Justice announced the arrest of the founder of Bitzlato, a now-shutteredpeer-to-peer crypto exchange.
Demand for leveraged bullish bets rises
Perpetual contracts, also known as inverse swaps, have an embedded rate that is usually charged every eight hours. Exchanges use this fee to avoid exchange risk imbalances.
A positive funding rate indicates that longs (buyers) demand more leverage. However, the opposite situation occurs when shorts (sellers) require additional leverage, causing the funding rate to turn negative.
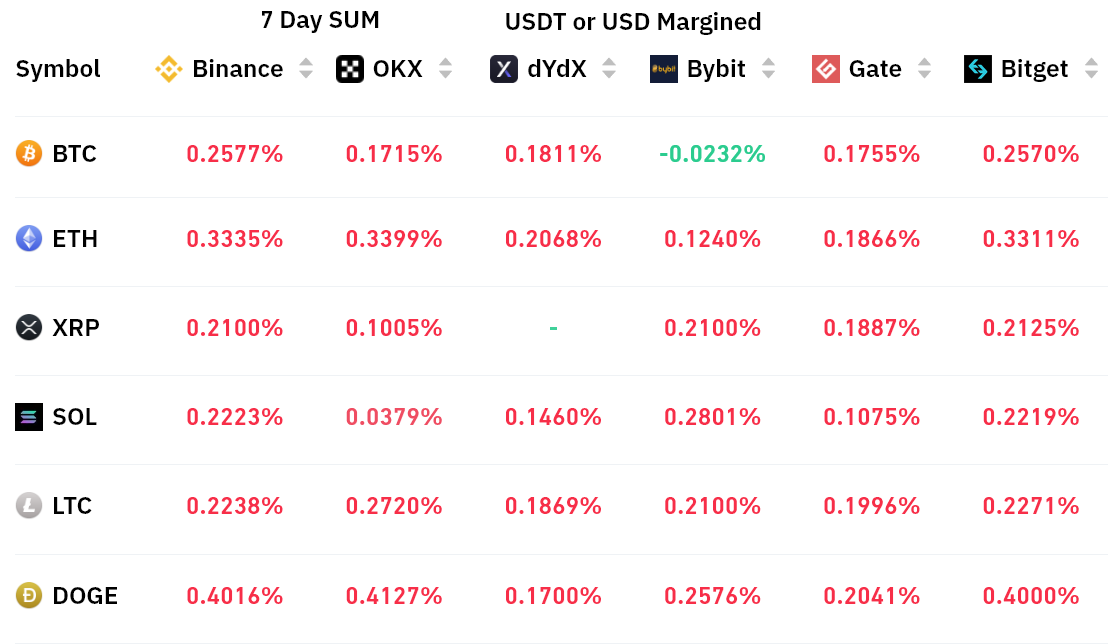

The seven-day funding rate was positive in every instance, meaning the data points to a higher demand for leverage longs (buyers) in the period. Still, being charged 0.25% per week to maintain their bullish trades opened should not be a significant concern for most investors.
Thus, traders should analyze the options markets to understand whether whales and arbitrage desks have placed higher bets on bullish or bearish strategies.
Investors are not afraid of dips, according to BTC options
Traders can gauge the market’s overall sentiment by measuring whether more activity is going through call (buy) options or put (sell) options. Generally speaking, call options are used for bullish strategies, whereas put options are for bearish ones.
A 0.70 put-to-call ratio indicates that put options open interest lag the more bullish calls by 30% and is therefore bullish. In contrast, a 1.40 indicator favors put options by 40%, which can be deemed bearish.


Even though Bitcoin failed to break the $21,500 resistance on Jan. 18, there were no signs of increased demand for downside protection. This becomes evident as the put-to-call volume remained below 0.80 the entire time, even after the negative 5.5% move on Jan. 18.
The neutral-to-bearish strategies remain strongly in demand in the BTC option markets, favoring call (buy) options by 23%.
Related: Compass Mining sued for losing Bitcoin mining machines bought by customers
Derivatives markets suggest support at the $930 billion level is strong
After solid gains over the past seven days, the cryptocurrency market continues to show resilience despite warnings of a “global financial meltdown” by BitMEX founder Arthur Hayes. This year “could be just as bad as 2022 until the Fed pivots,” Hayes wrote, calling that scenario his “base case.”
According to crypto derivatives metrics, there is hardly any sense of fear or absence of leverage buying demand after the total market capitalization first missed the opportunity to breach the $1 trillion mark. Those are encouraging signs, especially when combined with the technical analysis of the descending channel breakout.
Consequently, the odds favor the previous channel top at $930 billion becoming a strong support level. So, for now, even a downturn in traditional markets should not be a huge concern for crypto bulls, but investors should continue monitoring derivatives metrics.
The views, thoughts and opinions expressed here are the authors’ alone and do not necessarily reflect or represent the views and opinions of Cointelegraph.
This article does not contain investment advice or recommendations. Every investment and trading move involves risk, and readers should conduct their own research when making a decision.